If you’ve noticed bleeding gums, persistent bad breath, or other gum-related issues, you might be dealing with more than a simple oral health problem. Gum disease, or periodontal disease, is a condition that extends beyond the mouth, potentially affecting your entire body. Understanding how gum disease affects your health is critical, especially as more research uncovers links between this condition and systemic health problems. Regular checkups and periodontal treatment can make a significant difference in managing and improving your overall health.
At Columbia Smiles, under the care of Dr. Michael Hsu, we’re committed to providing personalized and comprehensive dental care. Let’s explore the causes and implications of gum disease and encourage you to prioritize oral health to protect your general well-being.
What Is Gum Disease?
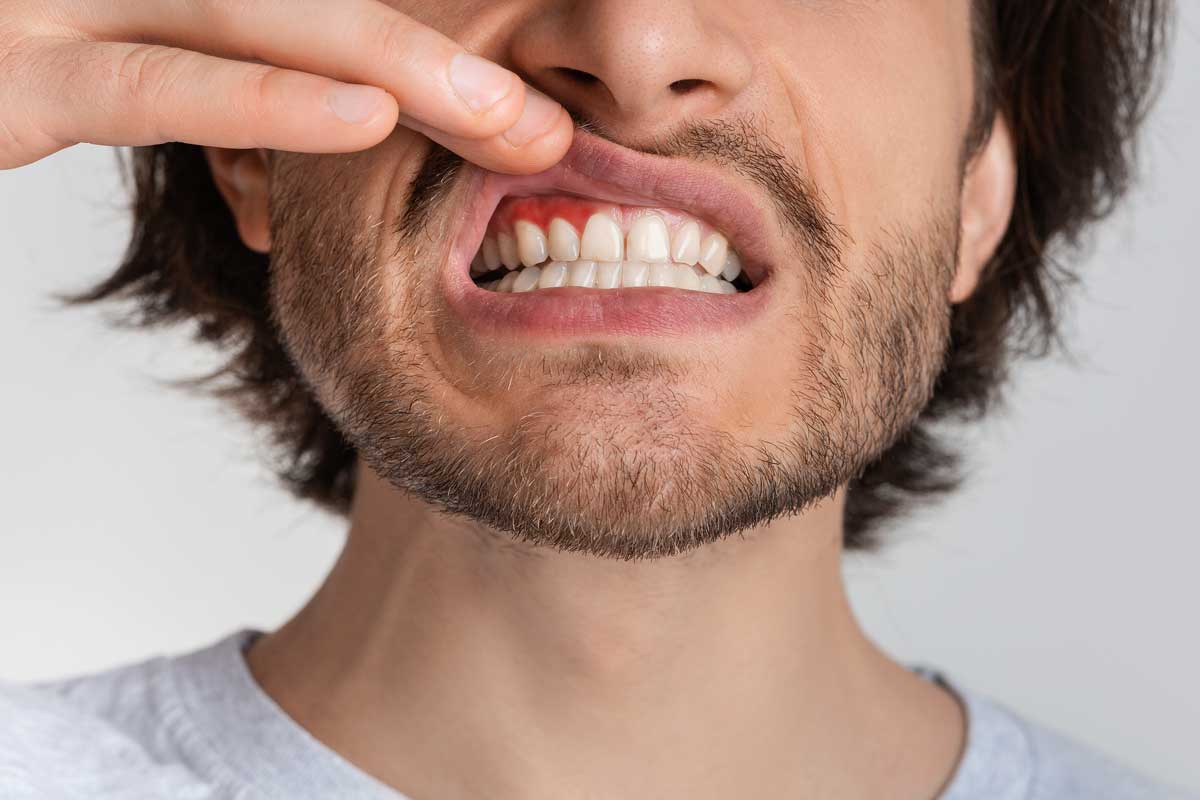
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a bacterial infection that affects the gums and the structures supporting your teeth, such as connective tissues and bone. It typically begins as gingivitis, a milder form of gum disease, characterized by red, swollen gums that bleed easily.
Without timely treatment, gingivitis can progress to periodontitis, a more severe condition that can lead to tooth loss and other health issues. Studies have also linked advanced gum disease to systemic health problems, including heart disease and diabetes.
Signs and symptoms of gum disease
Recognizing gum disease early can help prevent it from escalating. Common symptoms include:
- Red, swollen, or tender gums
- Bleeding during brushing or flossing
- Receding gums
- Persistent bad breath
- Loose teeth or changes in the way your teeth fit together
If you’re noticing one or more of these signs, it’s essential to seek professional care immediately to preserve both your oral and overall health.
What causes periodontal disease?
Periodontal disease develops when plaque, a sticky film of bacteria, builds up on your teeth. Without proper brushing and flossing, plaque hardens into tartar, leading to inflammation and infection in your gums. Over time, this can cause gum recession, tooth loss, and even affect your overall health.
Primary causes of gum disease
- Poor oral hygiene: Neglecting daily brushing and flossing allows plaque to accumulate, laying the foundation for gum disease. Over time, this can lead to swollen, bleeding gums and even more serious oral health issues if left untreated.
- Smoking or tobacco use: Tobacco products interfere with gum tissue’s ability to heal and increase the risk of infection.
- Hormonal changes: Fluctuations during pregnancy, menopause, or puberty can make gums more sensitive and susceptible to disease.
- Certain medications: Drugs that reduce saliva flow or cause gum enlargement (like antihistamines or blood pressure medications) can increase susceptibility to gum infections.
- Chronic conditions: Disorders such as diabetes weaken the body’s ability to fight infections, making gum disease more likely.
- Family history: Genetics can play a role, with some individuals inheriting a predisposition to periodontal disease.
Connection between gum health and whole-body health
Numerous studies have highlighted how gum disease affects your health beyond the oral cavity. Poor gum health is not an isolated issue—it has been linked to a variety of conditions affecting vital systems in the body, including:
Cardiovascular disease
Bacteria from gum infections can enter the bloodstream, triggering inflammation that may contribute to heart disease, clogged arteries, and even strokes. This connection underscores how proper oral care helps safeguard your cardiovascular system.
Diabetes
Diabetes and gum disease have a two-way relationship. People with diabetes are more likely to develop infections, including periodontal disease, while gum disease can make it more challenging to control blood sugar levels.
Pregnancy complications
Pregnant women with periodontal disease face a higher risk of premature birth and low birth weight. Hormonal changes during pregnancy further exacerbate gum inflammation. This makes maintaining good oral hygiene and seeking regular dental care even more critical during pregnancy.
Respiratory health
The bacteria present in gum disease can travel to the lungs, increasing the likelihood of respiratory infections such as pneumonia. This highlights the importance of maintaining good oral hygiene to not only protect your teeth but also safeguard your overall health.
Alzheimer’s disease
Emerging research suggests that chronic inflammation in the body, including gum disease, may be linked to cognitive decline and conditions like Alzheimer’s.
Understanding how gum disease impacts your health highlights the importance of maintaining good oral hygiene and seeking professional periodontal treatment when needed.
Can gum disease be cured?
The answer depends on the stage and severity of the condition. Gingivitis, the early stage of gum disease, is reversible with proper oral care and professional cleaning. However, once it progresses to periodontitis, management rather than curing becomes the focus. Advanced periodontal treatments, which may include scaling and root planing or surgery, can control the infection, restore gum health, and prevent further damage.
Regular dental checkups with Dr. Michael Hsu at Columbia Smiles are vital for detecting and addressing gum disease early, increasing the likelihood of effective management and recovery.
Can gum disease cause other health problems?
Yes, leaving gum disease untreated can escalate health risks beyond oral discomfort. These potential consequences underline how gum disease affects your health and why proactive care is essential. Diseases that can develop if gum disease is ignored include:
- Cardiovascular issues: Chronic inflammation from gum disease raises the risk of heart attacks and strokes. This occurs because inflammation can lead to the narrowing of arteries, reducing blood flow and increasing cardiovascular strain.
- Osteoporosis: Bone loss in the jaw caused by periodontitis can be linked to deterioration of bone density throughout the body. This connection highlights the importance of maintaining good oral health to support overall bone health.
- Diabetic complications: Poor gum health causes systemic inflammation, complicating blood sugar regulation. This connection highlights the importance of maintaining oral hygiene to support overall health and manage conditions like diabetes.
- Rheumatoid arthritis: Gum bacteria may trigger immune system reactions that aggravate joint inflammation. This connection highlights the importance of oral health in managing conditions like arthritis.
Clearly, the potential consequences of poor oral health extend far beyond the mouth, emphasizing the critical link between oral care and overall well-being. Maintaining good oral hygiene isn’t just about preserving your teeth. It’s a vital step in preventing serious systemic health issues and improving quality of life.
FAQs about gum disease and prevention
What are the risk factors for developing gum disease?
Some of the main risk factors include poor oral hygiene, smoking, genetics, hormonal changes (such as during pregnancy and menopause), certain medications that cause dry mouth, and underlying health conditions like diabetes and rheumatoid arthritis.
How can I prevent gum disease?
The best way to prevent gum disease is by practicing good oral hygiene habits. This includes brushing your teeth at least twice a day with fluoride toothpaste, flossing daily, using an antiseptic mouthwash, and visiting your dentist regularly for professional cleanings and check-ups.
It is also important to avoid risk factors such as smoking, maintain a healthy diet, and manage any underlying health conditions that may contribute to gum disease.
What are the signs of gum disease?
Common signs of gum disease include red, swollen, or tender gums, as well as bleeding during brushing or flossing. Other symptoms may include persistent bad breath, receding gums, loose teeth, or changes in your bite alignment. If you notice any of these signs, it’s important to consult your dentist promptly for evaluation and treatment.
Can gum disease affect overall health?
Yes, gum disease has been linked to various systemic health issues. Studies suggest that advanced gum disease, or periodontitis, may increase the risk of conditions such as heart disease, diabetes, and respiratory infections. Additionally, gum inflammation can exacerbate existing health problems. Maintaining good oral hygiene and addressing gum disease early can play a crucial role in supporting overall health.
Protect your health with periodontal treatment at Columbia Smiles
Gum disease is a widespread but preventable condition. Taking action now will help you avoid its far-reaching impacts on your health. At Columbia Smiles, Dr. Michael Hsu and his team can provide thorough periodontal exams and advanced treatments to promote optimal gum and overall health.
If you’ve been searching for how gum disease impacts your health, the good news is that help is just a call away. You don’t have to live with gum discomfort or worry about its broader health implications. Start taking control of your well-being today. Call us today at 410.690.4855 to make an appointment or use our convenient online contact form.